Aug 4, 2020|
JD Big Data Panorama: Chinese Brand Consumption Soars under COVID-19
by Ella Kidron
The 2020 Chinese Brand Development Report released by JD Big Data Research Institute and the Communication University of China (CUC) and other research organizations, as well as media groups such as Outlook Weekly, China Comment, and Credit100.com, looks at the key growth drivers and trends emerging in the consumption of domestic Chinese goods. The report, which is based on JD’s data, explores not only how domestic brands have performed, but also how social e-commerce and the consumption of services continues to drive reliance on domestic brands.
It is no secret that international brands are a bright spot for JD.com. As a platform that emphasizes high quality and authenticity, imported brands are well-loved by the e-commerce giant’s over 380 million consumers, as was demonstrated during this year’s 618 Grand Promotion.
While international brands remain a huge growth driver, domestic brands, which have proven their worth and reliability under the pressure of COVID-19, continue to gain the trust of JD’s high quality consumption base across China.
80% of brands on JD realizing over RMB 100 million yuan in H1 are Chinese brands
According to the data, in the first half of 2020, 80% of the brands on JD realizing over RMB 100 million yuan in sales were Chinese brands. Chinese brands also accounted for nearly 90% of brands whose sales have increased by more than 50%. On the whole, the improvement and growth rate of Chinese brands is clear.
Growth of Chinese brands faster than that of imported brands
In 2019, the year-on-year growth rate of the number of Chinese brand goods, the number of orders placed and the order volume was more than 20% higher than that of imported brands. Under the influence of COVID-19, in the first quarter of 2020, this number reached more than 30%. Looking at the growth rate of the transaction volume of Chinese brands vs. imported brands, the growth rate of the proportion of Chinese brands in categories such as maternal and child, sports, and personal care has been high. This demonstrates that consumption of Chinese brands in categories where trust is of particular importance continues to rise.
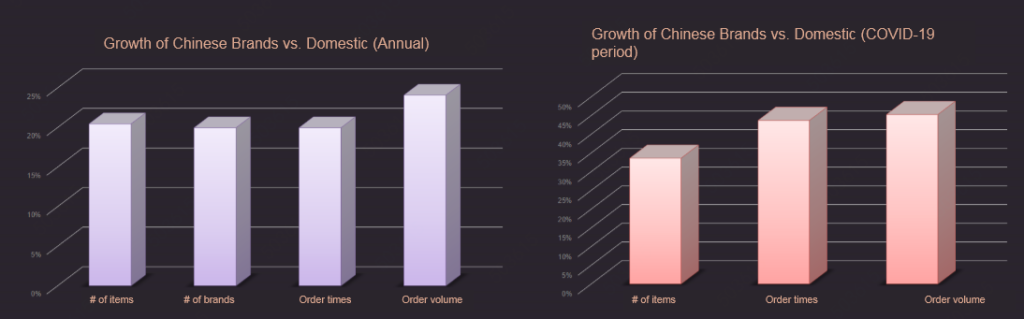
Chinese brands gain more consumers’ trust under COVID-19
In terms of the particular characteristics of consumption of domestic brands under COVID-19, the data reveals that for the first quarter of 2020, transaction volume of Chinese computers and office supplies grew 109% YOY, among which computers grew 194%. Chinese brand computer and office category notebooks, printers and other supplies accounted for the large increase in proportion as compared with 2019, among which the transaction volume growth of notebooks exceeded 30%.
Domestic fresh food products played an essential role in ensuring supply in the pandemic, transitioning from a complementary to comprehensive role. In the first quarter of 2020, transaction volume of domestic fresh food increased by 156% compared with the same period last year, among which transaction volume of meat (pork, beef and mutton), vegetables, poultry and eggs increased by 655%, 183% and 166% respectively YOY. Compared with the first quarter of 2019, domestic fresh food categories with the highest increases included pork, beef and mutton, prepared dishes, and instant food, among which the growth of transaction volume of pork, beef and mutton exceeded 20%, outpacing fresh produce and seafood, and leaping to the top of the fresh category.
Chinese brand health and protection products have also seen a rise. In the first quarter of 2020, transaction volume of domestic masks increased 10 times year-on-year, while transaction volume of homecare, masks and blood glucose meters increased significantly compared with the first quarter of 2019, becoming the top three health-related categories. The increase makes sense given the limited mobility of people during COVID-19 and the inconvenience of hospital visits, leading them to rely more on homecare and remote assistance.
The “acquaintance effect” in social shopping channels
The public health emergency of COVID-19 has brought new opportunities for development thanks to social e-commerce. The “acquaintance effect”, high popularity of daily necessities are among the main characteristics of social channel consumption. The data shows that, affected by the epidemic, consumers have increased their dependence on trusted relationships among acquaintances, thus directly promoting social e-commerce consumption based on personal relationships. Social e-commerce orders increased by more than 60% in the first quarter of 2020 compared with the same period last year. At the same time, the number of social e-commerce orders from the northern regions of the country, which are more sensitive to the acquaintance effect, increased significantly compared with the same period last year.
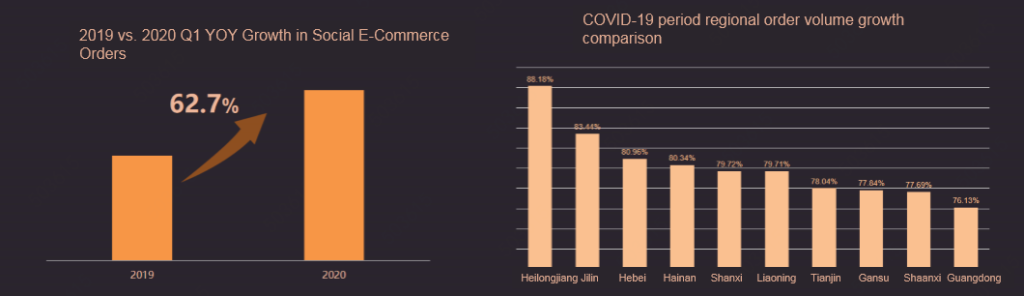
Social channels provide users with “more approachable consumption”, boosting the consumption potential of low- and medium-priced goods. Under the influence of COVID-19, small- and medium-sized domestic brands rely on cost-to-performance advantages to expand their user bases, and the new user effect for these brands is demonstrably higher than that of their imported brand counterparts. Compared with the same period in previous years, orders of fresh food, household cleaning and paper products, kitchen utensils and other products increased significantly. In terms of user group portraits, social e-commerce participaiton of village and town residents, enterprise employees and other groups is relatively high, thanks to the emphasis of these groups on performance-to-price ratio as well as the strong interpersonal relationships in the social environment. Social e-commerce is based on emotional trust, and this sense of trust can be very effective for brand building.
Online consumption of domestic goods expands from “things” to “services”
The increasing maturation of online-to-offline (O2O) models is leading to the rapid growth of the scale of service-oriented consumption of Chinese brands. According to the report, in 2019, the overall scale of service-oriented consumption of domestic brands more than tripled, compared with the same period the previous year, satisfying consumers’ diversified service needs. Among services, the auto-aftermarket is setting the pace, with vehicle maintenance and repair, ETC (the leading automated toll payment provider in China), car decor, washing and other services in consumers’ good graces. Renovation and installation services have become a highlight of online consumption. As consumers pay more attention to home quality, interior decoration has increased significantly, as high as 20-50 times. In addition, during the COVID-19 period, overall sales of “agency services” increased fivefold compared with the same period in 2019. There is a clear indication that online services will continue to prosper and become a new driving force for economic growth.
Lower-tier city penetration remains key focus
Lower-tier city penetration remains the most important growth point for domestic goods. According to the report, from 2019 to the first quarter of 2020, e-commerce channels continued to help Chinese brands penetrate the lower-tier markets. In the 5th and 6th tier cities, Chinese brands accounted for a higher proportion of consumption. Transaction volume of Chinese brands in the lower-tier markets also increased more than that of the same period last year. Domestic brand consumption in the first-tier markets is also strong, indicating that more users with high consumption power have significantly increased their awareness and trust of domestic products.







 Dr. Shen: Positive Consumption Growth is Important for China’s Economy in H2 2020
Dr. Shen: Positive Consumption Growth is Important for China’s Economy in H2 2020



